
Technical SEO, a Beginner's Guide
In this final article in our SEO for Beginners series, we look at ways to improve your website’s online visibility by tackling its technical components, also known as Technical SEO.
What is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO refers to a set of techniques used to optimize a website so that it can be more effectively scanned and ranked by search engines like Google.
Unlike on-page SEO, Technical SEO doesn’t look at a page’s content, but rather its underlying form and setup. If certain technical requirements are met, the website’s ranking in search results can (and usually will) improve.
While technical SEO is, as the name suggests, technical in nature, don’t let it intimidate you! There are a number of strategies that you can implement without needing to be an experienced developer. Let’s review some of them now!
7 Technical SEO Tips to Improve Your Website’s Rankings
- Add SSL for Site Security
- Make your Site Mobile friendly
- Improve Site Speed
- Avoid Duplicate Content
- Create a Sitemap
- Validate the Website’s Code
- Enhance Search Results With Structured Data
1. Add SSL for Site Security
Secure Socket Layer “SSL”, is the technology used to encrypt information between a website and its visitors. A website with SSL enabled will have an “s” in the https at the beginning of their website address; and will show a secure padlock next to the URL bar in a browser.
Alternatively, sites without SSL will show “not secure” next to the URL bar in a browser.
Beginning in 2018, Google gave preferential treatment to sites using SSL across all their pages. Adding an SSL certificate to a site is pretty simple. Hosting providers often bundle them with hosting plans and even provide automatic installations and renewals.
Simply installing an SSL certificate, however, won’t mean that a website is actually using https for all its content automatically. So make sure to force the use of https across the entire website!
2. Make Your Site Mobile-Friendly
A responsive site is one that adapts to fit different screen sizes, including PCs, tablets and smartphones. As smartphones count for nearly 50% of global web traffic, having a responsive site is incredibly important. So important that Google now does mobile first indexing, which means that it looks at the mobile version of a site first when determining how relevant the website could be to its users.
Many content management systems (such as WordPress) and site builders (such as Weebly) are designed to automatically create a responsive version of a site when building the desktop version. But even these don’t always provide perfect results. One of the best (and free) ways to test the mobile friendliness of a site is to use Google Search Console. Search Console will scan sites for errors under Mobile Usability.
If any errors are found Search Console will show where the errors are along with the most common ways to fix them.
For web designers interested in adding responsiveness to their site, here are Google’s guidelines for Responsive Web Design Basics.
3. Improve Site Speed
Most people really hate waiting for pages to load. This is clearly seen through bounce rate, where people visit a site but leave after looking at only a single page. A study by Google shows that long load times dramatically affect people’s willingness to explore a site.
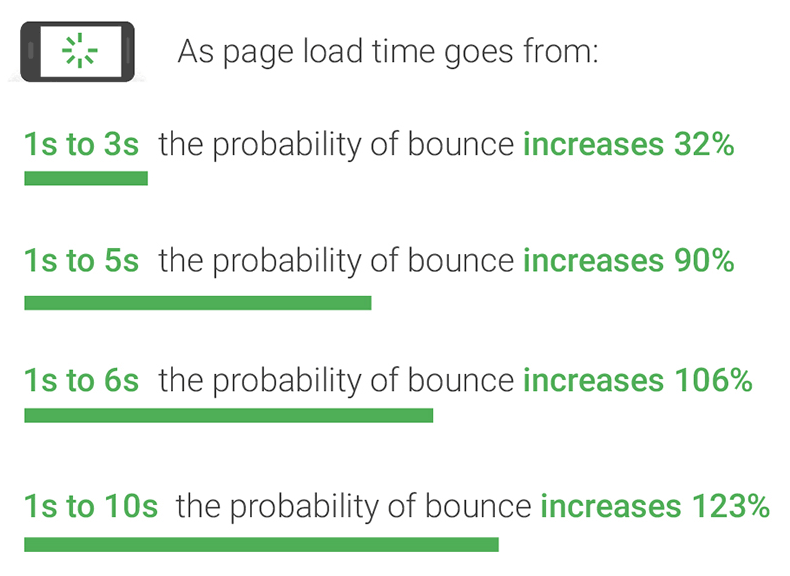
Image from Think With Google
Long load time of a page (page speed) not only discourages visitors; search engines also factor speed when ranking a site.
To investigate site speed, type a site’s address into GTmetrix or Google’s PageSpeed insights to see its speed score. Both tools are free and provide detailed guides for what needs improvement and how to get better results.
A quick way to improve a website’s performance is to choose a web host that offers website acceleration systems, like Web Hosting Canada’s LiteSpeed Caching. With a process called static & dynamic caching, load times for complex websites can be reduced by as much as 500%!
4. Avoid Duplicate Content
Google defines duplicate content as:
Substantive blocks of content within or across domains that either completely match other content or are appreciably similar. Mostly, this is not deceptive in origin.”
Search engines dislike duplicate content because they cannot easily decide which web page to show in the results and which version was plagiarized. Because of this, neither of the duplicate pages does as well as it should in search results. This in turn is a problem for site owners as the important backlink signals are often split between the duplicate content, making the ranking signal for the page weaker than it otherwise would be. In extreme cases, duplicate content can even cause your entire website (or specific content from within your website) to be removed from Google.
Luckily there are two free tools which will allow you to uncover duplicate content on your site, as well as find instances of other websites plagiarizing your content.
Find Duplicate Content Within Your Site
Siteliner will scan your site and show you how similar the different pages are to one another, as a percentage (0% being no similarities, 100% being duplicate content). Many of your pages will have a small percentage of duplication because websites often reuse the same footer, menu and/or sidebar. This is nothing to worry about. What you will need to pay attention to are pages that have high percentages of similarity.
When you find duplicate content you can either delete one of the duplicates or you can rewrite the content so that they are not so similar.
For Duplicate Content Plagiarized By Other Sites
CopyScape will take a page and scan the Internet for content that is the same or similar, on other sites. Some of the results will show pages that only have a few similar sentences to the page searched. This is normally not a major concern, and can be ignored in most cases. However, if you find content elsewhere that is very similar (or identical) to yours, then we recommend you act fast. Copyscape offers advice on what actions to take if another site appears to have plagiarized your content.
5. Create a Sitemap
A sitemap is a special file that lists all your website’s pages, along with the relationships between them. Unlike your web pages, sitemaps are read by machines, not humans. Search engines like Google will read your sitemap in order to better understand the different sections of your website.
Without a sitemap, search engines will still try to understand how your website is set up by reading through your entire website. This is slower and less effective than simply checking a single location.
For example, if you create a link to a new page within your site and don’t use a sitemap, Google will need to visit each of your pages until it finds the one with the new link, reads the new page, and recognizes it as new content on your site. This process is considerably longer than reading a single sitemap. As a result, using and maintaining an accurate sitemap helps Google add new pages (or updated existing pages) in its search engines results faster.
There are multiple free tools to create XML sitemaps. A good one is xml-sitemaps.com which will scan a website and create a sitemap of up to 500 pages at no charge. Simply copy and paste your website’s address, click start and a downloadable file will be created.
Google also provides a list of sitemap generators.
Apps like WordPress make the process of creating and maintaining Sitemaps easier with plugins like Yoast SEO, which do all the work for you automatically as you create or modify your content.
After adding an XML Sitemap to the site, you can notify Google by submitting its link (usually looks like example.ca/sitemap.xml) in Search Console, under Sitemaps.
6. Validate the Website’s Code
No matter how you’ve built your website, it will contain underlying code called HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) and styling code called CSS (Cascading Style Sheets). Search engines like Google can penalize a website’s ranking in search results if it has trouble interpreting its code, which can happen if the code contains errors.
The W3C Markup Validator Service and CSS Validation Service are great free tools to check your site’s code. Simply enter your page’s address and click Check.
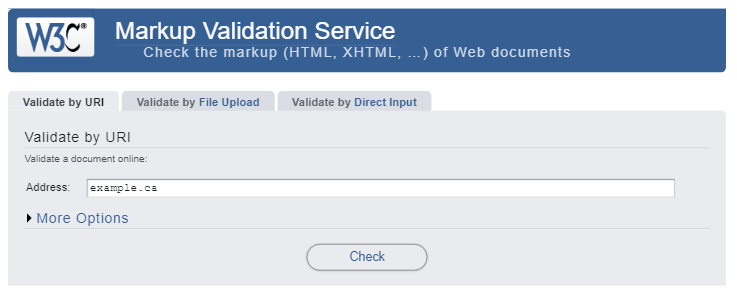
The tool will generate a list of warnings and errors and what to do about them. Some of the corrections (like removing a stray tag or character) could be quickly done by anyone with a summary understanding of HTML/CSS, whereas more complex corrections should be mandated to a website professional.
7. Enhance Search Results With Structured Data
When someone performs an online search, certain results show more information than others. For example, some results can show a company’s reviews or ratings while others don’t.
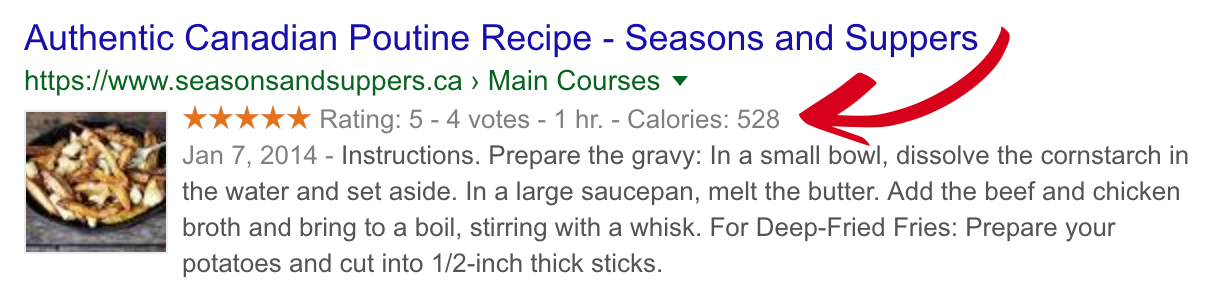
This is known as a rich result and happens thanks to structured data (also called schema markup). Not only can it help a result stand out from a list of similar results but it also provides more information to search engines, which in turn provide more information to visitors directly in search results.
For a detailed look at structured data and how to use it, read our article Increase your Google Visibility with Structured Data & Rich Results.
Optimize Away, Young SEO Jedi!

By following these 7 steps, you’ll be well on your way to improving your website’s Technical SEO which, in turn, should help improve your website’s overall ranking in search results.
This article also completes our SEO Guide for Beginners series. Assuming you’ve been reading from the start, you know have the basic knowledge needed to help put your website near the top of the search results. Congratulations! You are now a promising new SEO Jedi.
But don’t be swayed by the dark side! SEO magic doesn’t happen overnight. Good SEO is ongoing, long term work. It starts with selecting the right keywords, creating quality content, tweaking it for search engines, increasing its popularity through link building, and ensuring your website is technically sound. Beware of SEO services that promise instant results; they’re either lying or grossly exaggerating what they can do!
So go forth, young Jedi, and put your newly acquired SEO knowledge to work for you!
Happy optimizing,


Comments
Leave a Reply Laisser un commentaire
Leave a Reply Laisser un commentaire
Also on the WHC Blog

WordPress Categories and Tags: Organise your Blog!
If you manage your own website, you’re probably already aware that publishing new, useful content on a regular basis is an important part of increasing your website’s visibility and improving its rankings in search engine...
Read full article
WordCamp Montreal 2019: Here’s what You Missed!
The WHC team was excited to be a gold sponsor of WordCamp MTL 2019. We’ve got the round-up of what went down this past weekend at the event, in case you missed it! 2 Days. 45 Presentations. 17 Sponsors. 400 Attendees. With...
Read full article






Thank you for this article, Marc! There is also an alternative tool for generating XML sitemaps Octopus.do
Hope you’ll find it helpful.